Network Simulator
The Network Simulator tool allows you to test your multiplayer game in less-than-ideal network conditions, enabling you to discover issues in simulated real-world scenarios and fix them before they surface in production. It facilitates simulating network events, such as network disconnects, lag spikes, and packet loss.
The tool exposes configurable network parameters, such as packet delay and packet loss, that allow you to control the network conditions. It also bundles common configurations of those parameters together as presets.
You can use the Network Simulator component to test different network conditions and create custom network scenarios. These utilities include:
- Disabling the network connection
- Triggering a lag spike
- Changing the current configuration preset
You can also use the Network Simulator SDK to create custom network scenarios that can automatically trigger network events (such as a lag spike) at specific frequencies and intervals. To help you get started, it includes several example network scenarios.
Note: All parameters exposed through the Network Simulator tool work with the Unity Transport Protocol (UTP) simulator pipeline stage.
Requirements
The only requirement for using Network Simulator is Unity Editor version 2022.2 and later and the following package dependencies.
Package dependencies
| Dependency | Version | Package name |
|---|---|---|
| Unity Transport | 2.0.0 or later | com.unity.transport >= 2.0.0 |
| Netcode for GameObjects | 1.1.0 or later | com.unity.netcode.gameobjects >= 1.1.0 |
Get started
To get started with the Network Simulator:
- Add the following packages:
- Tools 1.1.0 or later
- Network for GameObjects 1.1.0 or later
- Unity Transport 2.0.0 or later
- Add the NetworkSimulator Component to any GameObject that persists across scenes.
Trigger a network disconnect
You can trigger a network disconnect in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Connection to Disconnected. See the Disconnect scenario example.
Trigger a lag spike
You can trigger a simulated lag spike in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Duration of the lag spike (ms), then selecting Trigger.
Tip: You can trigger lag spikes through code with the NetworkSimulator.TriggerLagSpike API or you can write a Network Scenario that triggers it. See the Lag spike scenario example to learn how.
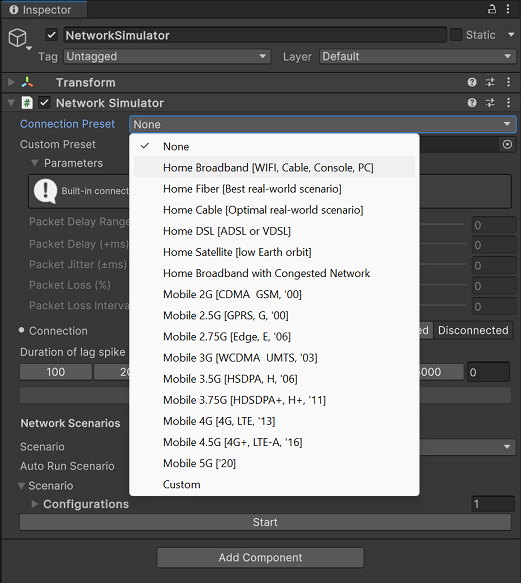
Use a Network Simulator Preset
The Network Simulator tool comes packaged with configuration presets that simulate common network conditions, such as a home broadband connection or a mobile 3G connection. To use one of the configuration presets:
- Select the NetworkSimulator component from the Hierarchy tab.
- Set the Connection Preset field to the configuration you want to use.
Create a Network Simulator Preset
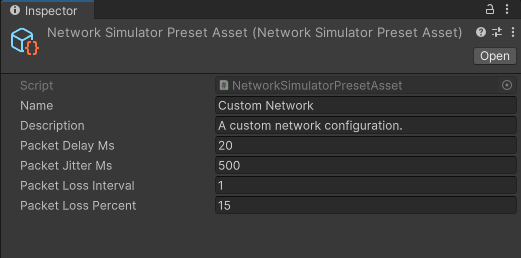
The Network Simulator tool allows you to create any number of custom network configuration presets. To create a custom network configuration preset:
- Right-click on the Assets folder in the Project tab.
- Select Create > Multiplayer > NetworkSimulatorPresetAsset.
- Select the NetworkSimulatorPreset from the Assets folder.
- Edit the parameters in the Inspector tab. The parameters allow you to set the name, description, packet delay, packet jitter, and packet loss (as a percentage and interval).
To use a custom Network Simulator Preset:
- In the Inspector tab, set the Connection Preset to Custom.
- Set the Custom Preset field to the preset asset you created.
Once you select the custom preset asset, you can edit it live from the Inspector tab by adjusting the parameters.
Use a Network Scenario
The Network Simulator tool supports NetworkScenarios. A NetworkScenario is a way to script how you want to affect the network conditions at runtime. They allow you to change parameters and presets dynamically.
It comes packaged with a couple network scenarios presets, such as the Connections Cycle and Random Connections Swap.
Note: You can also create custom network scenarios.
To use a network scenario:
- Select the NetworkSimulator component from the Hierarchy tab.
- Under Network Scenarios in the Inspector tab, set the Scenario field to the network scenario you want to use.
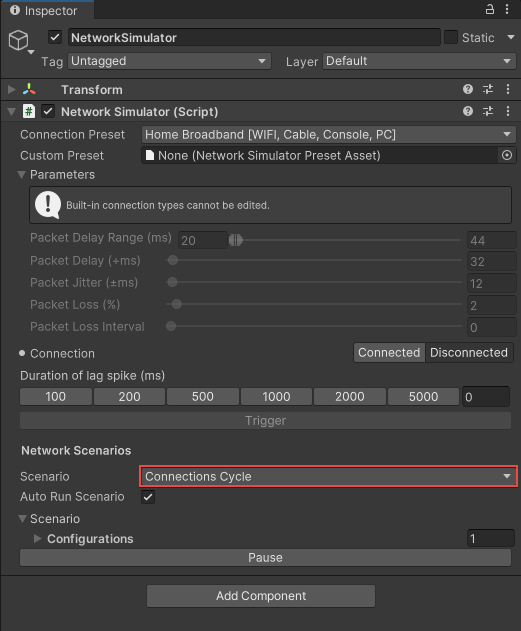
Tip: You can control whether the Network Scenario runs automatically by toggling the Auto Run Scenario checkbox. You can also set this option dynamically via code.
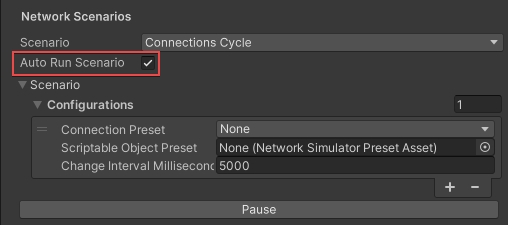
Connections Cycle
The Connections Cycle Network Scenario allows you to cycle through different network conditions at specific intervals. By default, it includes one cycle that’s set to None. To configure the Connection Cycle:
- From the Inspector tab, expand the Network Scenarios > Configurations section.
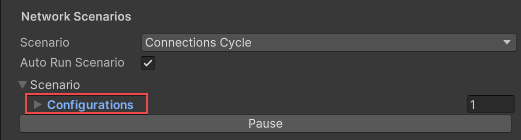
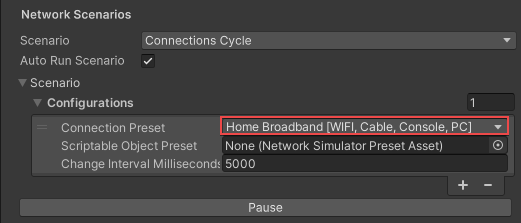
- Set the first Connection Preset to a built-in preset or a custom preset.
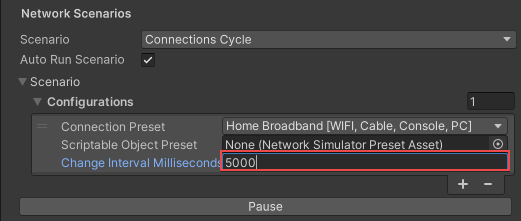
- Set the Change Interval Milliseconds field to the time to wait before switching to the next preset.
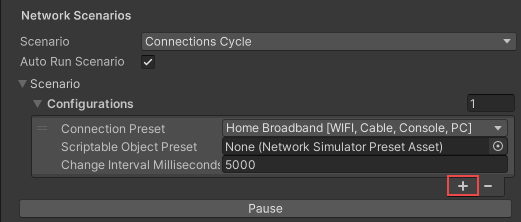
- Select the plus (+) symbol to add another cycle.
- Configure the next cycle as you see fit.
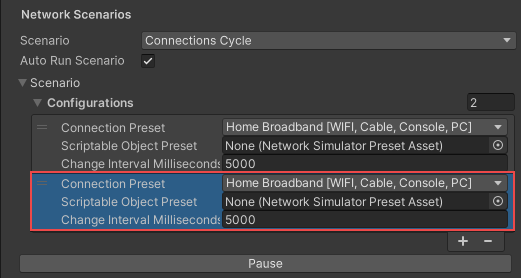
The Connections Cycle scenario cycles through the configurations list at the Change Interval until you use the Pause button to pause the connection cycling.
Random Connections Swap
The Random Connections Swap Network Scenario allows you to specify a set of network configuration presets to swap through at random. By default, it includes one cycle that’s set to None. To configure the Random Connection Swap:
- From the Inspector tab, expand the Network Scenarios > Configurations section.
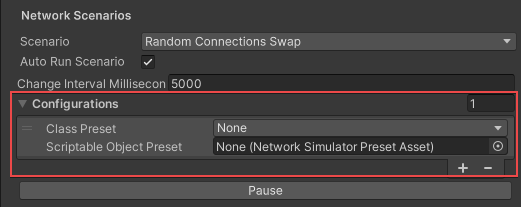
- Set the Class Preset to a built-in preset or a custom preset.
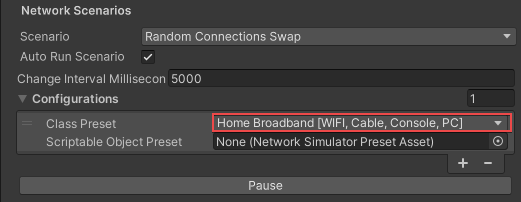
- Select the plus (+) symbol to add another configuration.
- Configure the configuration as you see fit.
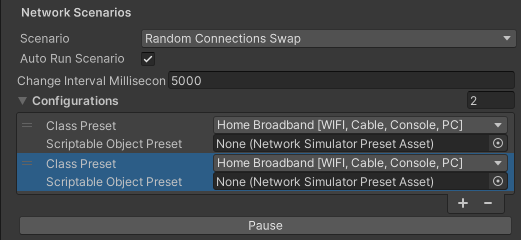
The Random Connections Swap scenario selects one of configurations from the list at random at the Change Interval until you use the Pause button to pause the connection cycling.
Network types
A network type is the general state of a user’s network connection. This section has the descriptions of the available Network Simulator preset configurations. These configuration presets fall into five categories:
- Home broadband connections
- Poor quality mobile connections
- Medium quality mobile connections
- Decent quality mobile connections
- Good quality mobile connections
Home broadband connections
A typical home broadband connection preset represents common connections from desktops, console platforms, and some mobile devices.
The Home Broadband Network Simulator presets simulates a good-quality mobile connection
Poor-quality mobile connections
A poor-quality mobile connection preset represents an extremely poor connection, entirely unsuitable for synchronous multiplayer gaming due to exceptionally high ping. However, it might work for some turn-based games.
The following Network Simulator presets simulate a poor-quality mobile connection:
Medium-quality mobile connections
A medium-quality mobile connection preset represents the minimum supported mobile connection for synchronous gameplay. Expect high pings, jitter, stuttering, and packet loss.
The Mobile 3.5G Network Simulator presets simulates a medium-quality mobile connection.
Decent-quality mobile connections
A decent-quality mobile connection preset represents a suitable network for synchronous multiplayer. However, the ping and overall connection quality and stability might result in poor player experience due to packet drops. Players might drop all packets in bursts of one to 60 seconds, so you must ensure you handle reconnections.
The following Network Simulator presets simulate a poor quality mobile connection:
Good quality mobile connections
A good quality mobile connection preset represents a mobile connection comparable to or better than a typical home broadband connection.
The Mobile 5G Network Simulator preset simulates a good-quality mobile connection
Network configuration presets
A network configuration preset is a bundle of Network Simulator parameters that simulate a common network connection type. This section covers the available Network Simulator configuration presets.
Home Broadband
The Home Broadband network simulation preset simulates a typical home broadband connection.
| Name | Home Broadband [WIFI, Cable, Console, PC] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a typical home broadband connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 32 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 12 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 2 |
Mobile 2G
The Mobile 2G network simulation preset simulates a typical 2G mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 2G [CDMA & GSM, '00] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a poor-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 400 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 200 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 2.5G
The Mobile 2.5G network simulation preset simulates a typical 2.5G (GPRS) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 2.5G [GPRS, G, '00] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a poor-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 200 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 100 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 2.75G
The Mobile 2.75G network simulation preset simulates a typical 2.75G (EDGE) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 3.75G [HDSDPA+, H+, '11] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 75 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 50 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 3G
The Mobile 3G network simulation preset simulates a typical 3G mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 3.75G [HDSDPA+, H+, '11] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 75 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 50 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 3.5G
The Mobile 3.5G network simulation preset simulates a typical 3.5G (HSDPA/H) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 3.75G [HDSDPA+, H+, '11] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 75 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 50 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 3.75G
The Mobile 3.75G network simulation preset simulates a typical 3.75G (HSPA+/H+) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 3.75G [HDSDPA+, H+, '11] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 75 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 50 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 3 |
Mobile 4G
The Mobile 4G network simulation preset simulates a typical 4G (LTE) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 4G [4G, LTE, '13] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 50 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 25 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 2 |
Mobile 4.5G
The Mobile 4.5G network simulation preset simulates a typical 4.5G (LTE+) mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 4.5G [4G+, LTE-A, '16] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a decent-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 50 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 25 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 2 |
Mobile 5G
The Mobile 5G network simulation preset simulates a typical 5G mobile connection.
| Name | Mobile 5G ['20] |
|---|---|
| Description | Simulates a good-quality mobile connection. |
| Packet delay (ms) | 1 |
| Packet jitter (ms) | 10 |
| Packet loss interval | 0 |
| Packet loss percent | 2 |
Network events
The following sections cover common network connection events and problems you can simulate with the Network Simulator.
Disconnects
A network disconnect is a disruption or termination of the connection between the sender and the receiver.
You can trigger a network disconnect in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Connection to Disconnected. See the Disconnect scenario example.
Lag spikes
A lag spike refers to a temporary increase in network latency. Some of the most common causes of lag spikes include overburdened CPUs, temporary network disconnects, and unreliable connections with high jitter.
You can trigger a simulated lag spike in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Duration of the lag spike (ms), then selecting Trigger. See the Lag spike scenario example.
Latency
Network latency measures the time it takes a packet to travel across a network in milliseconds (ms). Players experience high latency (sometimes called “lag”) when the time delay between the server (or host) sending the information and the client receiving the information creates communication bottlenecks or an undesirable playing experience.
You can trigger control the simulated network latency in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Packet Delay (ms) parameter.
Note: A common method of measuring the latency of a network connection is through ping messages. Pings are small network packets that you can use to measure the time it takes a packet to reach its destination in milliseconds. High ping often equates to high latency.
Packet loss
Packet loss occurs when packets fail to reach their destination when transmitted across a network. It’s typically measured as a percentage of packets lost or the frequency of packets dropped.
You can trigger control the simulated packet loss in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Packet Loss Interval and the Packet Loss (%) parameters.
Jitter
Jitter is the variation in packet delays (latency) measured in milliseconds (ms). High-quality network connections typically have reliable and consistent latency. However, poorer-quality network connections experience high variations in latency, which can create an inconsistent or poor experience for players. These high variations in latency can cause issues such as flickering displays, stuttering, further packet delays, and additional CPU usage.
You can trigger control the simulated network jitter in the Unity Editor with the Network Simulator component by setting the Packet Jitter (ms) parameter.
Instability
An unstable network connection might consist of intermittent network issues, such as network disconnects, packet loss, jitter, and latency.
See the Unstable connection scenario example.
Network scenarios
Network scenarios are built-in (or custom) presets for network types that simulate a specific scenario, such as intermittent lag spikes. They allow you simulate a variable combination of issues and automatically switching configuration presets.
You can use the Network Simulator SDK to create custom network scenarios that automatically trigger network events (such as a lag spike) at specific frequencies and intervals.
The code samples in this section showcase how you can build custom network simulator scenarios.
Lag spike scenario
The following code snippet shows using NetworkScenarioTask to create a custom network scenario that simulates a connection with lag spikes. See LagSpikeScenarioWithAsyncTask.cs.
Disconnect scenario
The following code snippet uses NetworkScenarioBehaviour to create a custom network scenario that simulates a connection with frequent player disconnects. See DisconnectScenarioWithMonoBehaviour.cs.
Unstable connection scenario
The following code snippet shows using NetworkScenarioTask to create a custom network scenario that simulates an unstable connection. See UnstableConnection.cs.
Affect connection parameters using Animation Curves scenario
The following code snippet uses NetworkScenarioBehaviour to create a custom network scenario that simulates multiple connection problems. It dynamically changes multiple connection parameters using Animation Curves. See ConnectionParametersWithCurves.cs.
The sample scenario showcases a dynamic scenario using an animation curve loop with variable packet delays, packet jittering, and packet loss.