High Level Terminology
Learn more about essential terms and concepts.
Networking Transport Layer
The transport layer collects message segments from applications, and transmits them into the network. The transport layer is also responsible for the management of error correction, providing quality and reliability to the end user.
This layer enables the host to send and receive error corrected data, packets or messages over a network
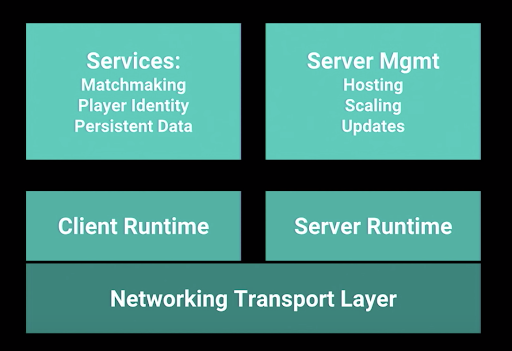
Client Runtime
Is the active software and instructions executed while your applications are running on your local client. This includes mobile devices and desktop computers using a client application.
Server Runtime
Is the active software and instructions executed while your applications are running on your server. This includes physical and virtual servers running hosted services and software communicating with additional services and clients.
Netcode
Is a blanket term for anything that somehow relates to networking in online games; netcode is a term most commonly used by gamers when discussing synchronization issues between clients and servers.
Client
Is a network client that connects an individual user to the server, used mainly in multiplayer video games. It collects data such as score, player status, position and movement from a single player and sends it to the server, which allows the server to collect each individual's data and show every player in game.
Server
Is a server which is the authoritative source of events in a multiplayer video game. The server transmits enough data about its internal state to allow its connected clients to keep their own accurate version of the game world for display to players. They also receive and process each player's input
Hit Registration
This is how a shooter determines if your shot hit something. There are two main forms of hit registration.
There are more than just two cases. The non physics version of bullets via raycast is often also used for weapons with travel time such as snipers. Parabolas of bullets can be calculated without the need of a physics simulation.
Games where bullet travel time isn't a factor in close quarters combat can use a simple and fast form where bullets have no travel time.
Games where you need more complex and demanding bullet physics simulations for hit registration. Every projectile has a travel speed and trajectory, affected by various factors.
Hit registration can be done by your game client (client side), which then tells the server (or in p2p, the other clients) that you hit something.
Asymmetrical multiplayer
A type of gameplay in which players can have significantly different roles or abilities from each other; enough to provide a significantly different experience of the game.
Soft Asymmetry: Players have the same basic mechanics (such as movement and death), yet have different roles in the game.
Strong Asymmetry: One player/team may have one gameplay experience (or be in softly asymmetric roles) while the other player/team play in a drastically different way, with different mechanics and/or a different type of objective.